Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) have become vital players in the steel manufacturing game, offering an efficient and sustainable alternative to conventional methods. This article aims to provide a straightforward look into how these industrial workhorses operate, breaking down the essential components and processes that make them tick.
Classification
Generally speaking, electric arc furnace(EAF) can be classified into 2 types, that is AC arc furnace and DC arc furnace. Including, AC arc furnace that we will introduce has 3 electrodes.
Structure
Concretely speaking, it can reduce superficial area of heat dissipation, this is the reason why its shape looks like a ball. Figure 1 is schematic map for electric arc furnace, it can divided into 4 parts according to picture roughly: furnace body, tilting device, furnace lid and lifting device.
Furnace body: as its name implied, it is shell for electric arc furnace and it is used to hold furnace burden;
Tilting device: this device can tilt furnace forward and backward. It can be used to hold slags when it tilts forward 10 degrees approximately. Moreover, when it tilts about 30 degrees backward, can be used to tapping of molten steel. Frankly speaking, motor type and hydraulic type can drive tilting device.
Lifting device: it can help to adjust depth that electrode inserted in slag so that resistance can be adjusted. And it makes furnace rated power meet the requirement.
Operating Principle And Methods
Now, we talk about principle and methods roughly and simply.
Frankly speaking, an EAF is essentially a tall structure with a furnace shell, a movable roof, and a tilting platform. However, the real action happens with the electric arc, a powerful current passing between two graphite electrodes situated above the metal charge. This arc generates extreme temperatures, upwards of 3,000 degrees Celsius, melting the scrap metal within the furnace. Once the scrap is in, electric arc initiated.
As the arc heats up the scrap metal, it starts to melt and undergo a refining process. Impurities and unwanted elements are removed through chemical reactions or oxidation, leaving behind molten steel with the desired composition. Using scrap metal not only reduces the need for raw materials but also contributes to the sustainability of the steelmaking process.
To enhance steel quality, additional operations like lancing and alloying may be employed. Lancing involves injecting oxygen into the molten metal to remove carbon and other impurities. Alloying means adding specific elements to achieve desired steel properties, such as strength or corrosion resistance.
Once the refining process is complete, the molten steel is ready to be tapped. Tilting the furnace allows the liquid metal to flow out and be directed into ladles or casting machines. Precision in this step is crucial for determining the quality and consistency of the final steel product.
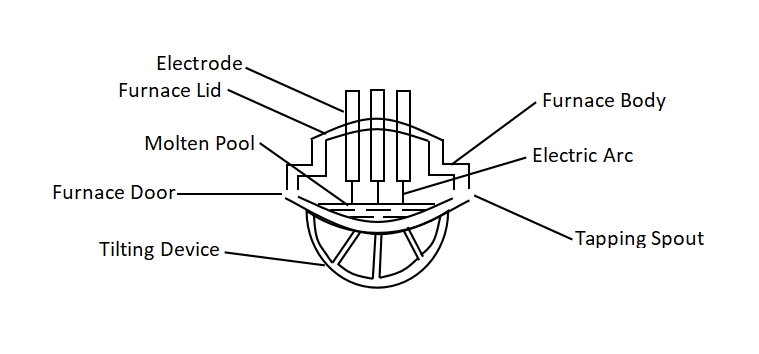
Fig. 1 Schematic map for electric arc furnace(EAF)
Conclusion
In the world of steel manufacturing, the electric arc furnace stands out as a practical solution. By using electricity to transform scrap metal into high-quality steel, EAFs contribute to sustainability and showcase innovation in metallurgy. As we continue to search for more sustainable and efficient steel production methods, the electric arc furnace remains a reliable and essential player in the industry.






